- Make sure the virtual desktop is using a SCSI controller. The master virtual desktop should be configured with a VMXNET 3 network adapter. When building the master virtual desktop, you will probably boot from an ISO.
- The SCSI ID of the logical unit number (LUN) changed. When this happened, the iSCSI storage repository became unplugged after a XenServer reboot. This article will help you identify if your iSCSI Storage Repository (SR) has changed SCSI IDs and provide steps to repair it. Note: This procedure requires Advance Level Xen Administration Skills.
- ESXi Windows SCSI控制器说明 王哥哥 ESXi 7.0 2021-01-25 276 次浏览 最近在看VM7.0的视频,发现了一个以前从来没注意过的问题,就是下图的SCSI控制器的问题 默认Windows都是一个lsi的scsi控制器,这个是兼容性最好,但是性能比较差,而性能最好的是我截图的这个VMware准.
- Citrix Scsi App
- Citrix Scsi Command
- Citrix Scsi & Raid Devices Driver Downloads
- Citrix Scsi File
- Citrix SCSI & RAID Devices Driver Download
- Citrix Scsi Login
With a full range of RAID storage products, NAS Solutions & iSCSI Solutions, they offers complete solutions for all of your needs. Proware by Unifosas products provide all storage interfaces including SAS, SCSI, iSCSI, SATA and Fibre Channel.
-->This article describes the issues that affect a Microsoft Windows Server-based domain controller (DC) that runs as a guest operating system in virtual hosting environments, and the things to consider when a DC runs in a virtual hosting environment.
Original product version: Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: 888794
Summary
A virtual hosting environment lets you run multiple guest operating systems on a single host computer at the same time. Host software virtualizes resources such as the following:
- CPU
- Memory
- Disk
- Network
- Local devices
By virtualizing these resources on a physical computer, host software lets you use fewer computers to deploy operating systems for testing and development, and in production roles. However, certain restrictions apply to an Active Directory DC that runs in a virtual hosting environment. These restrictions do not apply to a DC that runs on a physical computer.
This article discusses the things to consider when a Microsoft Windows Server-based DC runs in a virtual hosting environment. Virtual hosting environments include the following:
- Windows Server Virtualization with Hyper-V.
- VMware family of virtualization products.
- Novell family of virtualization products.
- Citrix family of virtualization products.
- Any product on the hypervisor list in the Server Virtualization Validation Program (SVVP).
For updated information about the current status of system robustness and security for virtualized DCs, see Virtualizing Domain Controllers using Hyper-V. The Virtualizing Domain Controllers article provides general recommendations that apply to all configurations. Many of the considerations that are described in that article also apply to third-party virtualization hosts. It might include recommendations and settings that are specific to the hypervisor that you are using. Topics include these:
- How to configure time synchronization for DCs.
- How to manage disk volumes for data integrity.
- How to take advantage of Generation ID support in restoration or migration scenarios.
- How to manage allocation and performance of RAM and processor cores on the virtual machine host.
Citrix Scsi App
Note
If you are using third-party virtualization hosts, consult the virtualization host documentation for specific guidance and recommendations.
This article supplements the Virtualizing Domain Controllers article by providing additional hints and considerations that were not in scope for the Virtualizing Domain Controllers article.
Things to consider when you host DC roles in a virtual hosting environment
When you deploy an Active Directory DC on a physical computer, certain requirements must be satisfied throughout the DC's lifecycle. The deployment of a DC in a virtual hosting environment adds certain requirements and considerations. These include the following requirements and considerations:

The Active Directory service helps preserve the integrity of the Active Directory database if a power loss or other failure occurs. To do this, the service runs unbuffered writes, and tries to disable the disk write cache on the volumes that host the Active Directory database and log files. Active Directory also tries to work in this manner if it's installed in a virtual hosting environment.
If the virtual hosting environment software correctly supports a SCSI-emulation mode that supports forced unit access (FUA), unbuffered writes that Active Directory performs in this environment are passed to the host operating system. If FUA is not supported, you must manually disable the write cache on all volumes of the guest operating system that host the Active Directory database, the logs, and the checkpoint file.
Note
- You must disable the write cache for all components that use Extensible Storage Engine (ESE) as their database format. These components include Active Directory, the File Replication Service (FRS), Windows Internet Name Service (WINS), and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
- As a best practice, consider installing uninterruptable power supplies on virtual machine hosts.
An Active Directory DC is intended to run Active Directory mode continuously as soon as it is installed. Do not stop or pause the virtual machine for an extended time. When the DC starts, end-to-end replication of Active Directory must occur. Make sure that all the DCs do inbound replication on all locally held Active Directory partitions according to the schedule that is defined on site links and connection objects. This is especially true for the number of days that is specified by the tombstone lifetime attribute.
If this replication does not occur, you might experience an inconsistency in the contents of Active Directory databases on DCs in the forest. This inconsistency occurs because knowledge of deletes persists for the number of days that is defined by the tombstone lifetime. DCs that do not transitively complete inbound replication of Active Directory changes within this number of days cause objects to linger in Active Directory. Cleaning up lingering objects can be time-consuming, especially in multi-domain forests that include many DCs.
To recover from user, hardware, software, or environmental problems, an Active Directory DC requires regular system state backups. The default useful life of a system state backup is 60 or 180 days, depending on the operating system version and the service pack revision that is in effect during the installation. This useful life is controlled by the tombstone lifetime attribute in Active Directory. At least one DC in every domain in the forest should be backed up on a regular cycle per the number of days that is specified in the tombstone lifetime.
In a production environment, you should make system state backups from two different DCs on a daily basis.
Note
When the virtual machine host takes a snapshot of a virtual machine, the guest operating system does not detect this snapshot as a backup. When the host supports the Hyper-V Generation ID, this ID would be changed when the image is started from a snapshot or replica. By default, the DC would consider itself to be restored from a backup.
Things to consider when you host DC roles on clustered hosts or when you use Active Directory as a back end in a virtual hosting environment
When your DCs run on clustered host servers, you would expect that they are fault tolerant. This same expectation applies to virtual server deployments that are not from Microsoft. However, there is one problem in this assumption: In order for the nodes, disks and other resources on a clustered host computer to autostart, authentication requests from the clustered host computer must be serviced by a DC in the clustered host computer's domain. Alternatively, part of the configuration of the clustered host must be stored in Active Directory.
To make sure that such DCs can be accessed during cluster system startup, deploy at least two DCs in the clustered host computer's domain on an independent hosting solution that is outside this cluster deployment. You can use physical hardware or another virtual hosting solution that doesn't have an Active Directory dependency. For more information about this scenario, see Avoid creating single points of failure.
These DCs on separate platforms should be kept online and be network-accessible (in DNS and in all required ports and protocols) to the clustered hosts. In some cases, the only DCs that can service authentication requests during cluster startup reside on a clustered host computer that is being restarted. In this situation, authentication requests fail, and you'll have to manually recover the cluster.
Note
Do not assume that this situation applies to Hyper-V only. Third-party virtualization solutions can also use Active Directory as a configuration store or for authentication during certain steps of VM startup or configuration changes.
Support for Active Directory DCs in virtual hosting environments
For more information about the supportability of hosting DCs in Microsoft and third-party virtual hosting environments, see Support policy for Microsoft software that runs on non-Microsoft hardware virtualization software.
- FAQ
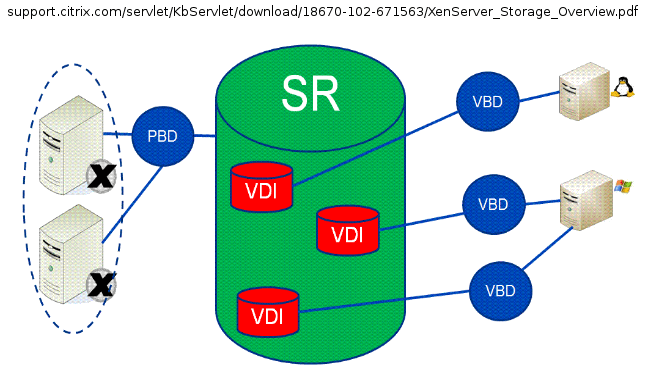
This article provides a generic overview of multipathing for Citrix XenServer 6.2, 6.5, and 7.0. For information about multipathing in XenServer 7.1 and later, see the Citrix XenServer Administrator Guide.
Basic Multipath ConfigurationDynamic multipathing support is available for Fibre Channel and iSCSI storage repositories (SRs). By default, multipathing uses round robin mode load balancing, so both routes will have active traffic on them during normal operation. You can enable or disable storage multipathing in XenCenter using the Multipathing tab on the server's Properties dialog.
Before you enable multipathing:
- Verify that multiple targets are available on your storage server.
- The server must be placed in Maintenance Mode; this ensures that any running virtual machines with virtual disks in the affected storage repository are migrated before the changes are made.
- Multipathing must be configured on each host in the pool. All cabling and, in case of iSCSI, subnet configurations must match the corresponding NICs on each host. For example, all NIC 3s must be configured to use the same subnet.
To Enable or disable Multipathing using XenCenter
The following section contains instructions on enabling and disabling Multipathing using XenCenter.
- In the XenCenter Resources pane, select the server and then put it into Maintenance Mode. There may be a short delay while XenCenter migrates any active virtual machines and unplugs the existing storage. If the server is a pool master, it will be disconnected and may disappear from the Resources pane temporarily while a new pool master is assigned. When the server reappears in the Resources pane with the icon, continue to the next step.
- On the General tab, click Properties and then click on the Multipathing tab.
- To enable multipathing, select the Enable multipathing on this server check box. To disable multipathing, clear the check box.
- Click OK to apply the new setting and close the dialog box. There is a short delay while XenCenter saves the new storage configuration.
- Take the server out of Maintenance Mode: select the server in the Resources pane, right-click, and then click Exit Maintenance Mode.
To Enable or Disable Multipath Using the xe CLI
- Stop all the VMs which are using virtual disks on the SRs, so that the SRs can be unplugged.
2. Unplug the PBDs related to such SRs for safety purposes. For every such SR:
3. Change multipath setting for the host setting the host's other-config:multipathing parameter:
# xe host-param-set other-config:multipathhandle=dmp uuid=host_uuid
4. Plug the PBDs back in:
- Repeat steps 1-4 for each server in the pool.
 Advanced Multipath Configuration
Advanced Multipath ConfigurationRedundant Disk Array Controller (RDAC) Configuration (XenServer 6.2 only)
RDAC configuration is required by many storage vendors. This configuration is related to IBM DS4xxx, however you can try it on other storage where RDAC is required.Important: This configuration may not work for certain storage types and is mostly experimental.
We recommend that you configure and test RDAC multipathing before placing your XenServer hosts into production.
The following section provides an example using IBM storage:
- Find out vendor and product type.
- The vendor option is usually the manufacturer, such as IBM.
- The product number can be found by using several tools or by asking the manufacturer. For example, if you have Qlogic Fibre Channel HBA you can use the “scli” tool to query the target and find out the product id.
# scli -t
Note: If 'scli' is not in your path, you can find it at the following location: /opt/QLogic_Corporation/QConvergeConsoleCLI/scli - Add the device into the devices section in the /etc/multipath.conf file. There are already some device sections included. Just add the new device at the beginning or the end of the existing section. The section should look like the following example. Note that there could be additional device sections within the devices section as shown in the following example:
devices {
vendor 'IBM'
product '1815'
prio_callout '/sbin/mpath_prio_rdac /dev/%n'
path_grouping_policy group_by_prio
failback immediate
path_checker rdac
hardware_handler '1 rdac'
user_friendly_names no
}
}
- Reload the multipath configuration. See the “Reload Multipath Configuration” section for more information.
- Show the multipath information. See the “Show multipath information” section for more information.
- Enable the mppVhda driver. Some storage devices require the use of the mppVhba driver, which is not enabled by default. Most of the IBM storage that requires RDAC need the driver to be enabled.
- Note: You can use wild cards in the product if the product option is too long. For example, “1723*”
Asymmetric Logical Unit Access (ALUA) for iSCSI Devices
Refer to the blog on XenServer 6.5 and Asymmetric Logical Unit Access (ALUA) for iSCSI Devices for information.Reload Multipath Configuration
Reload multipath configuration on each XenServer in the pool after any change to the /etc/multipath.conf file. Run the following command:# service multipathd restart
Citrix Scsi Command
Testing and Troubleshooting
Show Multipath Information
Run the following command to show the current multipath topology:# multipath -l
# multipath -ll
Run the following command to show the verbosity and print all paths and multipaths:
# multipath -v 2
Run the following command to refresh information what is supplied by previous commands:
# multipath -v 3
Note: In some cases, multipath -ll displays all the paths correctly and XenCenter may not display all paths that are connected. In such scenarios follow the instruction in the section 'Refresh Multipath information in XenCenter'.
Citrix Scsi & Raid Devices Driver Downloads
Refresh Multipath Information in XenCenter
If you notice that multipath -ll displays all the paths correctly and XenCenter shows you that some paths are not connected, you can refresh the information by running the following script:# /opt/xensource/sm/mpathcount.py
Citrix Scsi File
iSCSI - Testing and Troubleshooting Commands
Check open-iscsi service status:# service open-iscsi status
Restart open-iscsi service:
# service open-iscsi restart
Discover targets at given IP address:
# iscsiadm -m discovery -t sendtargets -p <ip_address_of_storage>
Log on to the target manually (The letter “l” stands for “logon”):
# iscsiadm -m node -T <iqn> -p <ip-address-of-the-storage> -l
See the disk and iSCSI ID in devices:
# ll /dev/disk/by-id/
You should be able to see the disk in this directory after a successful iSCSI logon. The long number is the SCSI ID. You can use it for sr-create or when manually creating PBD for iSCSI.
The following command provides a more concise output that includes the SCSI IDs.
# ll /dev/disk/by-scsid/
Log off the target (The letter “u” stands for “log off”):
# iscsiadm -m node -T <iqn> -p <ip-address-of-the-storage> -u
iSCSI - Not Every Path Available
You might experience an issue where only one path becomes active. Other paths are not connected. To resolve this issue, you can log on each path manually on the boot as explained in the following steps:You already have one active path on IP address 192.168.30.1.
Discover the other paths, for example:
# iscsiadm -m discovery -t sendtargets -p 192.168.31.1
# iscsiadm -m discovery -t sendtargets -p 192.168.32.1
# iscsiadm -m discovery -t sendtargets -p 192.168.33.1
Test to logon the other paths, for example:
# iscsiadm -m node -T <iqn> -p 192.168.31.1 -l
# iscsiadm -m node -T <iqn> -p 192.168.32.1 -l
# iscsiadm -m node -T <iqn> -p 192.168.33.1 -l
Now you should be able to see all the paths active in XenCenter or by running the following command:
# multipath -l
Implement the logon command in /etc/rc.local on every server in the pool as follows:
# sleep 30
# iscsiadm -m node -T <iqn> -p 192.168.31.1 -l
# iscsiadm -m node -T <iqn> -p 192.168.32.1 -l
# iscsiadm -m node -T <iqn> -p 192.168.33.1 -l
Fibre Channel Commands
General Information about HBA and SCSI
To examine some simple information about the Fibre Channel HBAs in a machine# systool -c fc_host -v
To look at verbose information regarding the SCSI adapters present on a system
# systool -c scsi_host -v
To see what Fibre Channel devices are connected to the Fibre Channel HBA cards
# systool -c fc_remote_ports -v -d
For Fibre Channel transport information
# systool -c fc_transport -v
For information on SCSI disks connected to a system
# systool -c scsi_disk -v
To examine more disk information including which hosts are connected to which disks
# systool -b scsi -v
Use the sg_map command to view more information about the SCSI map
# sg_map -x
To obtain driver information, including version numbers and active parameters
For Qlogic HBAs
# systool -m qla2xxx -v
For Emulex HBAs
# systool -m lpfc -v
Note: For more information about systool commands, see Red Hat Knowledgebase, Article ID: 9937 - Why is the /proc/scsi/qla2xxx/ or /proc/scsi/lpfc/ directory missing in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 and what has replaced it?
Qlogic HBA
Rescan QLogic HBA for available LUNs:# echo “- - -“ > /sys/class/scsi_host/host<number>/scan
(For more details see CTX120172 - How to Rescan the Qlogic Host Bus Adapter for New Logical Unit Numbers in XenServer)
Disks should appear in /dev/disk/by-id
# ll /dev/disk/by-id
Query Qlogic HBA for attached instances:
# scli -t
Query Qlogic HBA for LUNs
# scli -l <hba_instance_number_from_previous_command>
Removing HBA-based FC or iSCSI device entries
# echo '1' > /sys/class/scsi_device/<adapter>:<bus>:<target>:<lun>/device/delete
Emulex HBA
Citrix SCSI & RAID Devices Driver Download
Utility for Emulex HBA:# hbacmd
Display help to the command:
# hbacmd -h
Query Emulex HBAs:
# hbacmd listHBAs
List HBA attributes:
# hbacmd hbaattrib <wwpn_from_previous_command>
For example:
# hbacmd hbaattrib 10:00:00:00:c9:20:08:cc
List HBA port attributes:
# hbacmd portattrib <wwpn_from_previous_command>
For example:
# hbacmd portattrib 10:00:00:00:c9:20:08:cc
Note: If hbacmd is not in the path, you can find it at /usr/sbin/hbanyware/hbacmd
Citrix Scsi Login
Q: Do you support third-party handlers?A: Citrix only supports default device-mapper (dmp) from XenServer 6.5 onwards. In addition to default device-mapper (dmp), XenServer 6.2 also supports DMP RDAC, and MPP RDAC for LSI compatible controllers.
Q: To what extent do you support multipathing configurations?
A: Citrix only supports default configurations. However, you might change /etc/multipath.conf configuration file according to your requirements, or to vendor-specific settings and then reload the multipath configuration as explained in “Reload Multipath Configuration” section.
Q: Do you support the PowerPath handler?
A: No.
